Zip Heck
Categories: forensics
2020-07-24
by not_really
I zipped up the flag a few times for extra security.
https://files.uiuc.tf/flag.zip
The intended solution runs in under 10 minutes on a typical computer.
Author: kuilin
File mirror: flag.zip
I zipped up the flag a few times for extra security.
https://files.uiuc.tf/flag.zip
The intended solution runs in under 10 minutes on a typical computer.
Author: kuilin
File mirror: flag.zip
I actually had a computer normally extract this zip and it crashed a few times but eventually it was able to decode the zip successfully. So if someone didn’t know any better they could have done that and gotten the flag without any skill. But surprisingly this problem only has 12 solves.
I originally tried loop extracting the zip the normal way hoping I would get somewhere, but it seemed like it was taking forever.
import zipfile
import os
if not os.path.exists("temp"):
os.mkdir("temp")
while True:
with zipfile.ZipFile("flag.zip", "r") as flagZip:
flagZip.extractall("temp")
os.remove("flag.zip")
os.rename("temp/flag.zip", "flag.zip")
size = os.path.getsize("flag.zip")
print(f"now at size {size}b")
It all seems to be going fine until:
now at size 47098999b
now at size 47084853b
now at size 47075775b
now at size 47207829b
now at size 47207683b
now at size 47207537b
Wait a second, did the size just get bigger? It seems to decompress faster for a little bit before going slow again. Let’s investigate.
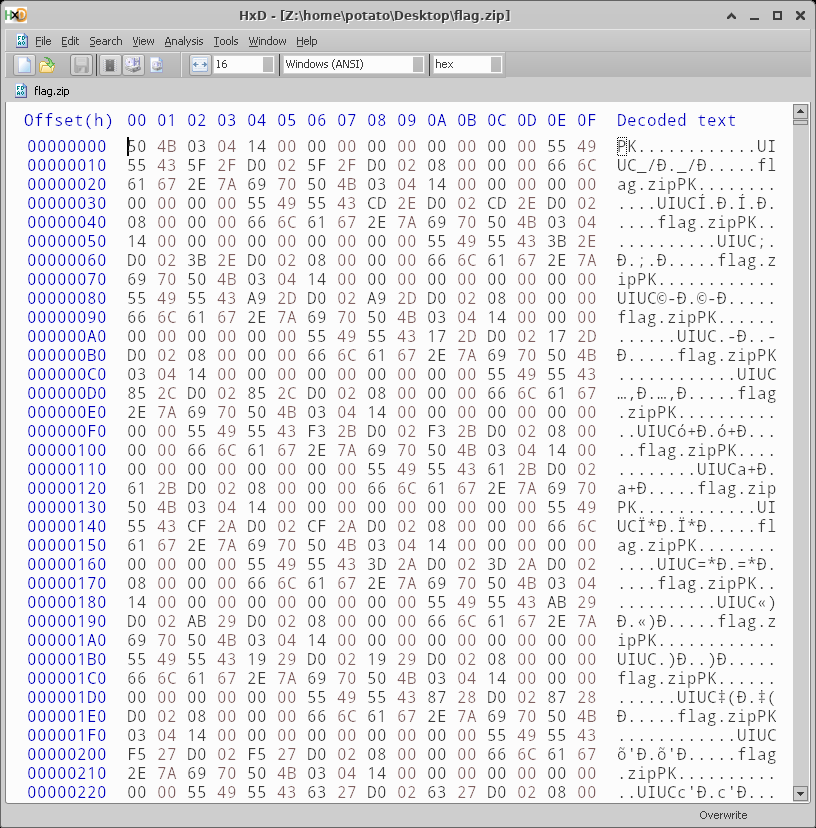
Hmm, isn’t zip supposed to compress this kind of stuff? But no, we see lots of flag.zip and UIUC. Let’s look in 7-zip.
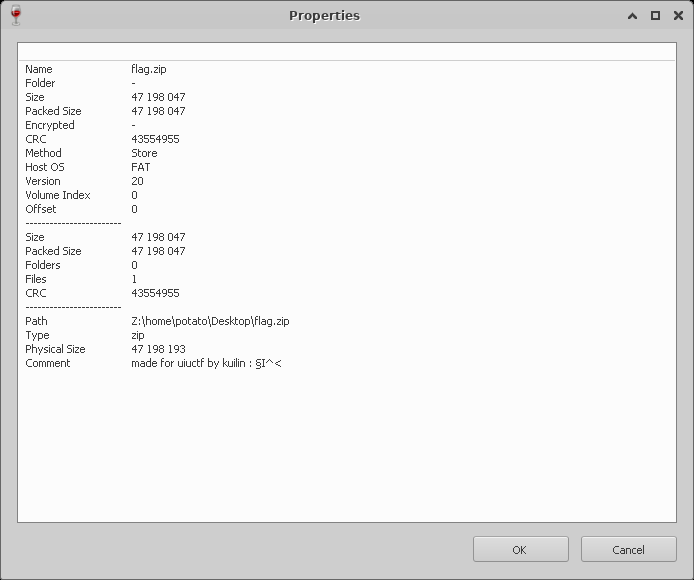
Ah, as I thought. It looks like instead of using the default Deflate method, we’re using Store. That means that there’s no compression here. Most likely we need to get rid of the chain of Store quicker than normally extracting would be.
The top of each uncompressed zip is 0x26 bytes:
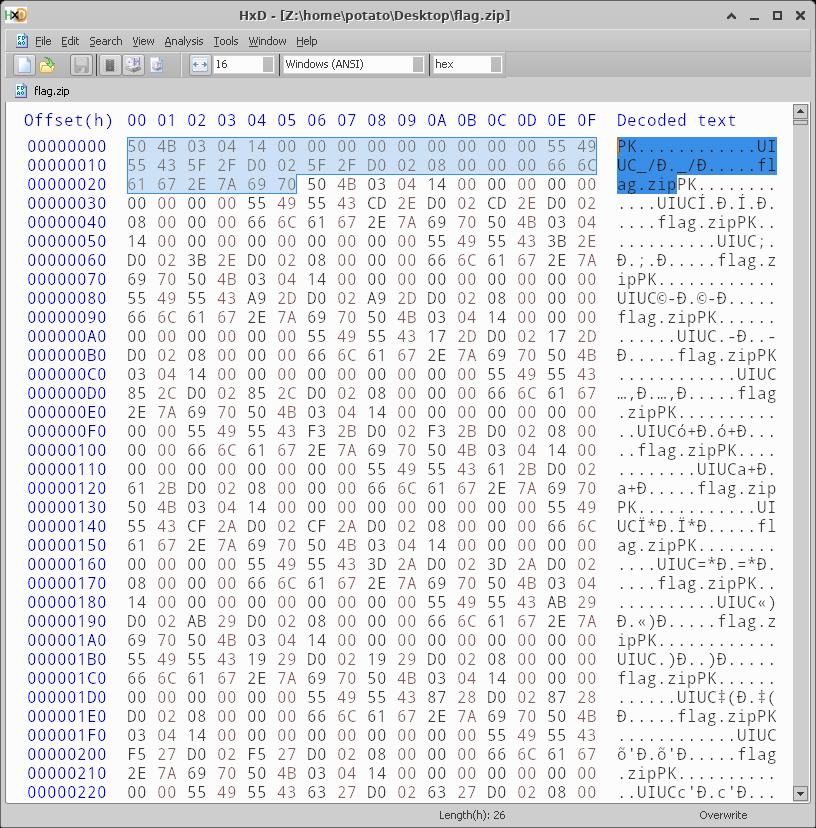
And the bottom is 0x6C:
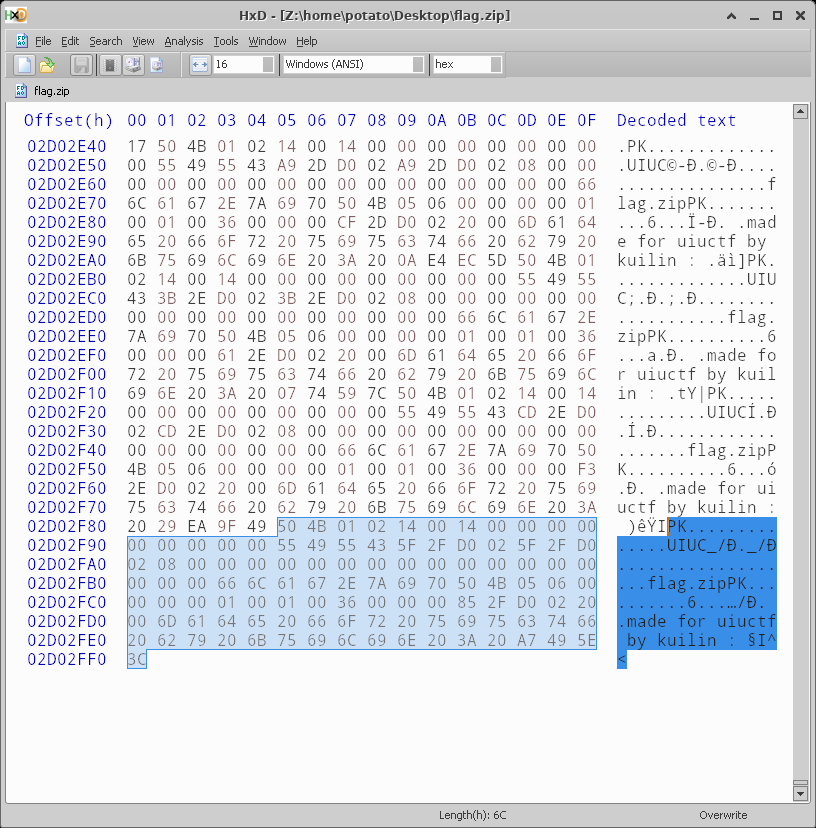
So now we need to know when to stop manually stripping the uncompressed bits off and go back to extractall for the Deflate parts.
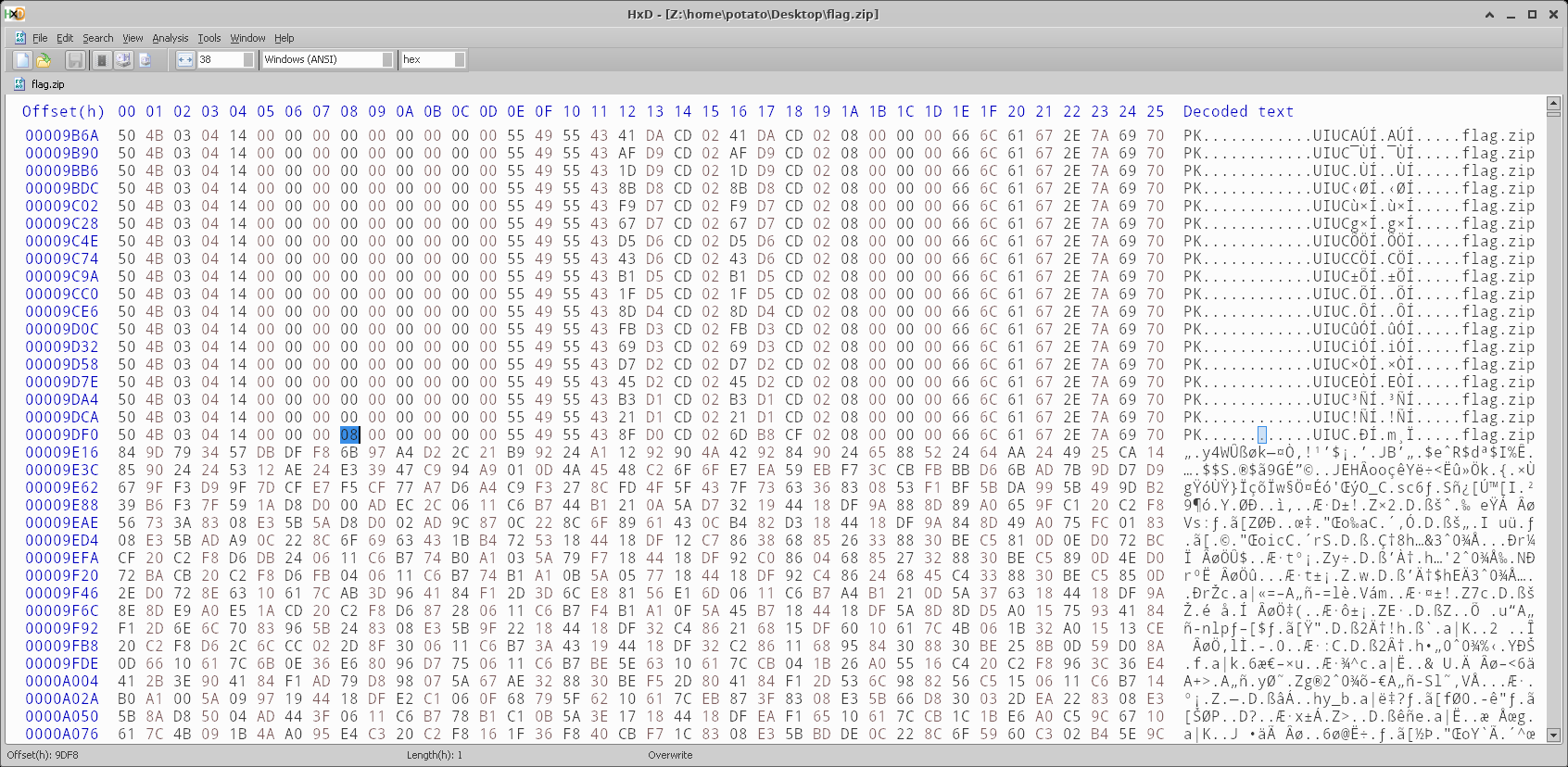
Looks like when it goes back to being compressed, this byte here is set to 0x08.
To ignore the Store zips, we’ll look at the first 0x08 bytes of the zip. If it’s a 0x00, we seek 0x26 bytes and check if the next byte is a 0x00 and so on. If it’s a 0x08, we move back to the beginning of the header and read the whole zip file. For every header there’s also a “footer” of 0x6C bytes, so the length of the zip file we’ll read is origSize - (0x26+0x6c) * storeHeadersRead.
Looks like we have everything we need, let’s write up the code.
import zipfile
import os
if not os.path.exists("temp"):
os.mkdir("temp")
while True:
size = os.path.getsize("flag.zip")
print(f"now at size {size}b")
with open("flag.zip", "rb") as flagZipBytes:
flagZipBytes.seek(0x08)
if flagZipBytes.read(1) == b'\x00': # store
print("detected store chain!")
count = 1
while True:
flagZipBytes.seek(0x08 + 0x26 * count)
if flagZipBytes.read(1) == b'\x08': # deflate
print(f"back to deflate (unzipped {count} times)")
# move back to beginning of zip header
flagZipBytes.seek(0x26 * count)
# original size - header - footer
sizeOfNewZip = size - (count * 0x26) - (count * 0x6c)
newFlagZipBytes = flagZipBytes.read(sizeOfNewZip)
with open("temp/flag.zip", "wb") as newFlagZip:
newFlagZip.write(newFlagZipBytes)
flagZipBytes.close()
os.remove("flag.zip")
os.rename("temp/flag.zip", "flag.zip")
break
else:
count += 1
with zipfile.ZipFile("flag.zip", "r") as flagZip:
flagZip.extractall("temp")
os.remove("flag.zip")
os.rename("temp/flag.zip", "flag.zip")
Once it throws an exception, check the temp folder for the flag.